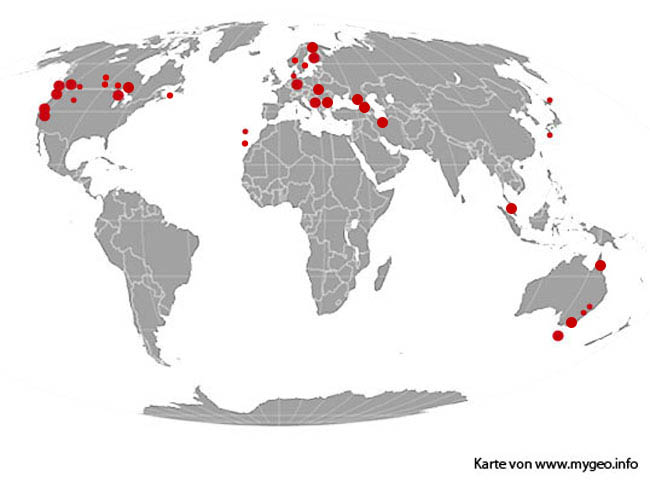
- AUSTRALIA: NEW SOUTH WALES
- AUSTRALIA: QUEENSLAND
- AUSTRALIA: TASMANIA
- Evercreech Forest Reserve
- Franklin-Gordon Wild Rivers National Park
- Lower Coles Road
- McDougall’s Road
- Reynold Falls Nature Recreation Area
- Styx Tall Trees Forest Reserve
- Tarkine
- AUSTRALIA: VICTORIA
- AUSTRIA
- BOSNIA-HERZEGOVINA
- BULGARIA
- Baiuvi dupki-Dzhindzhiritsa Nature ReserveNEW
- Boatin Strict Nature Reserve - NEW !!
- Dzhendema Strict Nature Reserve - NEW !!
- Parangalitsa Strict Nature Reserve - NEW !!
- Rila Monastery Forest Reserve - NEW !!
- Steneto Strict Nature Reserve - NEW !!
- CANADA: ALBERTA
- CANADA: BRITISH COLUMBIA
- Carmanah Walbran Provincial Park
- Clayoquot Sound Biosphere Reserve
- Glacier National Park
- MacMillan Provincial Park
- Pacific Rim National Park Reserve
- Yoho National Park
- CANADA: NOVA SCOTIA
- CANADA: ONTARIO
- Lake Superior Provincial Park
- Michipicoten parks
- Quetico Provincial Park
- Rainbow Falls Provincial Park
- CANADA: SASKATCHEWAN
- CROATIA
- CZECHIA
- DENMARK
- FINLAND
- Helvetinjärvi National Park
- Isojärvi National Park
- Kurjenrahka National Park
- Patvinsuo National Park
- Petkeljärvi National Park
- Pyhä-Häkki National Park
- Urho Kekkonen National Park
- Vätsäri Wilderness Area
- GEORGIA
- GERMANY
- Bavarian Forest National Park
- Fauler Ort Nature Reserve
- Hainich National Park
- Harz National Park
- Heilige Hallen Nature Reserve
- Jasmund National Park
- Müritz National Park
- Rhön Biosphere Reserve
- IRAN
- JAPAN
- MONTENEGRO
- PORTUGAL
- ROMANIA
- SLOVAKIA
- Boky National Nature Reserve
- Dobroč National Nature Reserve
- Havešová National Nature Reserve
- Stužica National Nature Reserve
- SPAIN
- SWEDEN
- UNITED STATES: CALIFORNIA
- Humboldt Redwoods State Park
- Kings Canyon National Park
- Mokelumne Wilderness
- Prairie Creek Redwoods State Park
- Sequoia National Park
- Yosemite National Park
- UNITED STATES: MICHIGAN
- UNITED STATES: WASHINGTON
- Goat Marsh Research Natural Area
- Mount Rainier National Park
- Olympic National Forest
- Olympic National Park
- UNITED STATES: WYOMING
Pyhä-Häkki National Park, Finland

Most of the forest in this park (13 km 2 ) has grown without noticeable human disturbance 1 . Thus, it is the largest primeval forest of southern Finland.
Before the introduction of modern fire suppression, the fire return interval in central Finland was approximately 50–120 years
2
. The last fire in the park was in 1921
1
. However, these fires were mostly of human origin; particularly in the period which began at the end of 1500’s and ended about 1850, the fire interval was much shorter than the natural one, which had been 200–500 years
3
. Gap-dynamics and surface fires were the dominant natural disturbance regime unlike, for example, in western Siberia and central Canada (see
![]() Prince Albert National Park
), where crown fires are dominant
4
.
Prince Albert National Park
), where crown fires are dominant
4
.
![]() Pinus sylvestris
(Scots pine) and
Pinus sylvestris
(Scots pine) and
![]() Picea abies
(Norway spruce) dominate.
P. sylvestris
is present everywhere from bogs to the driest areas; it is the most drought-tolerant and nutrient-stress-tolerant of the Eurasian boreal tree species
5
, and the thick bark of large individuals protects them from fire
4
. On dry soils, it maintains its dominance, but in the absence of fire, fire-intolerant and more shade-tolerant
5
P. abies
is invading mesic soils. The dark
P. abies
stands contrast with light
P. sylvestris
stands. The other large tree species of the park are
Picea abies
(Norway spruce) dominate.
P. sylvestris
is present everywhere from bogs to the driest areas; it is the most drought-tolerant and nutrient-stress-tolerant of the Eurasian boreal tree species
5
, and the thick bark of large individuals protects them from fire
4
. On dry soils, it maintains its dominance, but in the absence of fire, fire-intolerant and more shade-tolerant
5
P. abies
is invading mesic soils. The dark
P. abies
stands contrast with light
P. sylvestris
stands. The other large tree species of the park are
![]() Betula pendula
(silver birch),
Betula pendula
(silver birch),
![]() B. pubescens
(downy birch),
B. pubescens
(downy birch),
![]() Populus tremula
(common aspen) and on a few wet sites
Populus tremula
(common aspen) and on a few wet sites
![]() Alnus glutinosa
(black alder). You may have difficulties distinguishing between
B. pendula
and
B. pubescens
but other tree species are very easy to identify.
Alnus glutinosa
(black alder). You may have difficulties distinguishing between
B. pendula
and
B. pubescens
but other tree species are very easy to identify.
The park is located at an elevation of approx. 160–190 metres . Annual precipitation is 600 mm and average annual temperature 2.5°C. Off-trail hiking is very easy, apart from bogs. Camping is not allowed in the park but possible outside the park boundaries, like everywhere in Finland, Sweden and Norway.
References :
1 Pyhä-Häkin kansallispuisto. Metsähallitus.
2 Parviainen, J., Päivinen, R., Uuttera, J. & Varmola, M. (1999): Finland. In Parviainen, J. et al. (eds.): Research in Forest Reserves and Natural Forests in European Countries . EFI Proceedings No. 16, 1999.
3 Keto-Tokoi, P. & Kuuluvainen, T. (2010): Suomalainen aarniometsä. Maahenki.
4
Shorohova, E., Kneeshaw, D., Kuuluvainen, T. & Gauthier, S. (2011):
![]() Variability and Dynamics of Old-Growth Forests in the Circumboreal Zone: Implications for Conservation, Restoration and Management
.
Silva Fennica
45
(5).
Variability and Dynamics of Old-Growth Forests in the Circumboreal Zone: Implications for Conservation, Restoration and Management
.
Silva Fennica
45
(5).
5 Nikolov, N & Helmisaari , H. (1992): Silvics of the circumpolar boreal forest tree species. In Shugart, H. H. et al. (eds.): A Systems Analysis of the Global Boreal Forest , 13 – 84. Cambridge.
Official site:
http://www.nationalparks.fi/en/pyha-hakkinp
-

-
Picea abies (Norway spruce) forest. Also Populus tremula (common aspen), extreme left, and dead Betula sp. (birch, white trunk), left. Elev. 170 m.
-

-
The tallest and most heavily wooded stand of the park with Pinus sylvestris (Scots pine, with coarse lower bark and reddish upper bark) and Picea abies (Norway spruce), both up to 35 m tall. Also shrub-like Sorbus aucuparia (European rowan). Elev. 170 m.
-

-
Forest on dry soil with Pinus sylvestris (Scots pine, foreground and red trunks in the background), Picea abies (Norway spruce, with dark foliage) and Betula pendula (silver birch, with white bark). Elev. 175 m.
-

-
Kotajärvi at 165 m. Pinus sylvestris (Scots pine) forest. Left also Picea abies (Norway spruce); right also small Betula pubescens (downy birch).
-

-
Pinus sylvestris (Scots pine) forest at 175 m regenerated after wildfire in 1855. Also Picea abies (Norway spruce) sapling, right.
-

-
Boggy forest with Alnus glutinosa (black alder, dark trunks), Betula pubescens (downy birch, white trunks), Picea abies (Norway spruce, foliage on the right) and Pinus sylvestris (Scots pine, red trunks, background) at 165 m.
-

-
Alnus incana (grey alder), foreground. Also Pinus sylvestris (Scots pine), left, and Picea abies (Norway spruce), right.