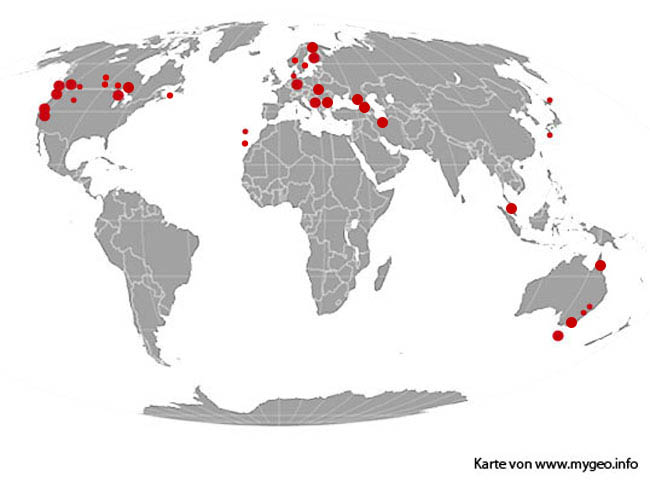
- AUSTRALIA: NEW SOUTH WALES
- AUSTRALIA: QUEENSLAND
- AUSTRALIA: TASMANIA
- Evercreech Forest Reserve
- Franklin-Gordon Wild Rivers National Park
- Lower Coles Road
- McDougall’s Road
- Reynold Falls Nature Recreation Area
- Styx Tall Trees Forest Reserve
- Tarkine
- AUSTRALIA: VICTORIA
- AUSTRIA
- BOSNIA-HERZEGOVINA
- BULGARIA
- Baiuvi dupki-Dzhindzhiritsa Nature ReserveNEW
- Boatin Strict Nature Reserve - NEW !!
- Dzhendema Strict Nature Reserve - NEW !!
- Parangalitsa Strict Nature Reserve - NEW !!
- Rila Monastery Forest Reserve - NEW !!
- Steneto Strict Nature Reserve - NEW !!
- CANADA: ALBERTA
- CANADA: BRITISH COLUMBIA
- Carmanah Walbran Provincial Park
- Clayoquot Sound Biosphere Reserve
- Glacier National Park
- MacMillan Provincial Park
- Pacific Rim National Park Reserve
- Yoho National Park
- CANADA: NOVA SCOTIA
- CANADA: ONTARIO
- Lake Superior Provincial Park
- Michipicoten parks
- Quetico Provincial Park
- Rainbow Falls Provincial Park
- CANADA: SASKATCHEWAN
- CROATIA
- CZECHIA
- DENMARK
- FINLAND
- Helvetinjärvi National Park
- Isojärvi National Park
- Kurjenrahka National Park
- Patvinsuo National Park
- Petkeljärvi National Park
- Pyhä-Häkki National Park
- Urho Kekkonen National Park
- Vätsäri Wilderness Area
- GEORGIA
- GERMANY
- Bavarian Forest National Park
- Fauler Ort Nature Reserve
- Hainich National Park
- Harz National Park
- Heilige Hallen Nature Reserve
- Jasmund National Park
- Müritz National Park
- Rhön Biosphere Reserve
- IRAN
- JAPAN
- MONTENEGRO
- PORTUGAL
- ROMANIA
- SLOVAKIA
- Boky National Nature Reserve
- Dobroč National Nature Reserve
- Havešová National Nature Reserve
- Stužica National Nature Reserve
- SPAIN
- SWEDEN
- UNITED STATES: CALIFORNIA
- Humboldt Redwoods State Park
- Kings Canyon National Park
- Mokelumne Wilderness
- Prairie Creek Redwoods State Park
- Sequoia National Park
- Yosemite National Park
- UNITED STATES: MICHIGAN
- UNITED STATES: WASHINGTON
- Goat Marsh Research Natural Area
- Mount Rainier National Park
- Olympic National Forest
- Olympic National Park
- UNITED STATES: WYOMING
Mokelumne Wilderness, California, USA
Most of this wilderness area (426 km
2
) is located along the crest and western high slopes of the Sierra Nevada, though it does extend slightly east of the crest. The most common forest trees are
![]() Pinus monticola
(western white pine),
Pinus monticola
(western white pine),
![]() P. contorta
var.
murrayana
(Sierra lodgepole pine),
P. contorta
var.
murrayana
(Sierra lodgepole pine),
![]() Abies magnifica
(red fir) and
Abies magnifica
(red fir) and
![]() Tsuga mertensiana
(mountain hemlock).
Tsuga mertensiana
(mountain hemlock).
![]() Pinus albicaulis
(whitebark pine) is common close to the tree limit at approx. 2500–3000 m. The fourth largest
Pinus albicaulis
(whitebark pine) is common close to the tree limit at approx. 2500–3000 m. The fourth largest
![]() Pinus ponderosa
(ponderosa pine) by volume grows near the park’s lower limit at approx. 1600 m
1
. Tree species diversity is low and most species are easy to identify. Annual precipitation on the western slopes is approx. 1300 mm.
Pinus ponderosa
(ponderosa pine) by volume grows near the park’s lower limit at approx. 1600 m
1
. Tree species diversity is low and most species are easy to identify. Annual precipitation on the western slopes is approx. 1300 mm.
Off-trail hiking is generally easy. Dispersed camping is allowed in more remote areas.
References:
1 /d0efbeed55a0d93f499ac407099560f5/viewtopic.php?f=69&t=6489#p29559
Official site:
http://www.fs.usda.gov/recarea/stanislaus/recreation/recarea/?recid=16839